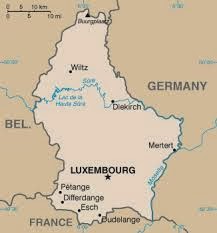
Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. It comprises two principal regions: the Oesling in the north as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland ("good country") in the south. Luxembourg has a population of 524,853 (as of October 2012) and an area of 2,586 square kilometres (998 sq mi), making it one of the smallest sovereign nations in Europe.
As a representative democracy with a constitutional monarch, it is headed by a grand duke and is the world's only remaining grand duchy. Luxembourg is a developed country, with an advanced economy and the world's second highest GDP (PPP) per capita (after Qatar), according to the World Bank. Its central location has historically made it of great strategic importance to numerous powers, dating back to its founding as a Roman fortress, its hosting of a vitalFrankish castle during the Early Middle Ages, and its role as a bastion for the Spanish Road between 16th and 17th centuries.
Luxembourg is a member of the European Union, NATO,OECD, the United Nations, and Benelux, reflecting its political consensus in favour of economic, political, and military integration. The city of Luxembourg, which is thecapital and largest city, is the seat of several institutions and agencies of the EU. On 18 October 2012, Luxembourg was elected to a temporary seat on the United Nations Security Council for the first time in its history. The country will serve on the Security Council from 1 January 2013 until 31 December 2014. Reflecting its geographic position, Luxembourg's culture is a fusion of Romanic and Germanic Europe, borrowing customs from each. Subsequently, Luxembourg is a trilingual country: Luxembourgish, Frenchand German are official languages. Although a secular state, Luxembourg is predominantly Roman Catholic.